Classifying Alzheimer Patients With GFNet
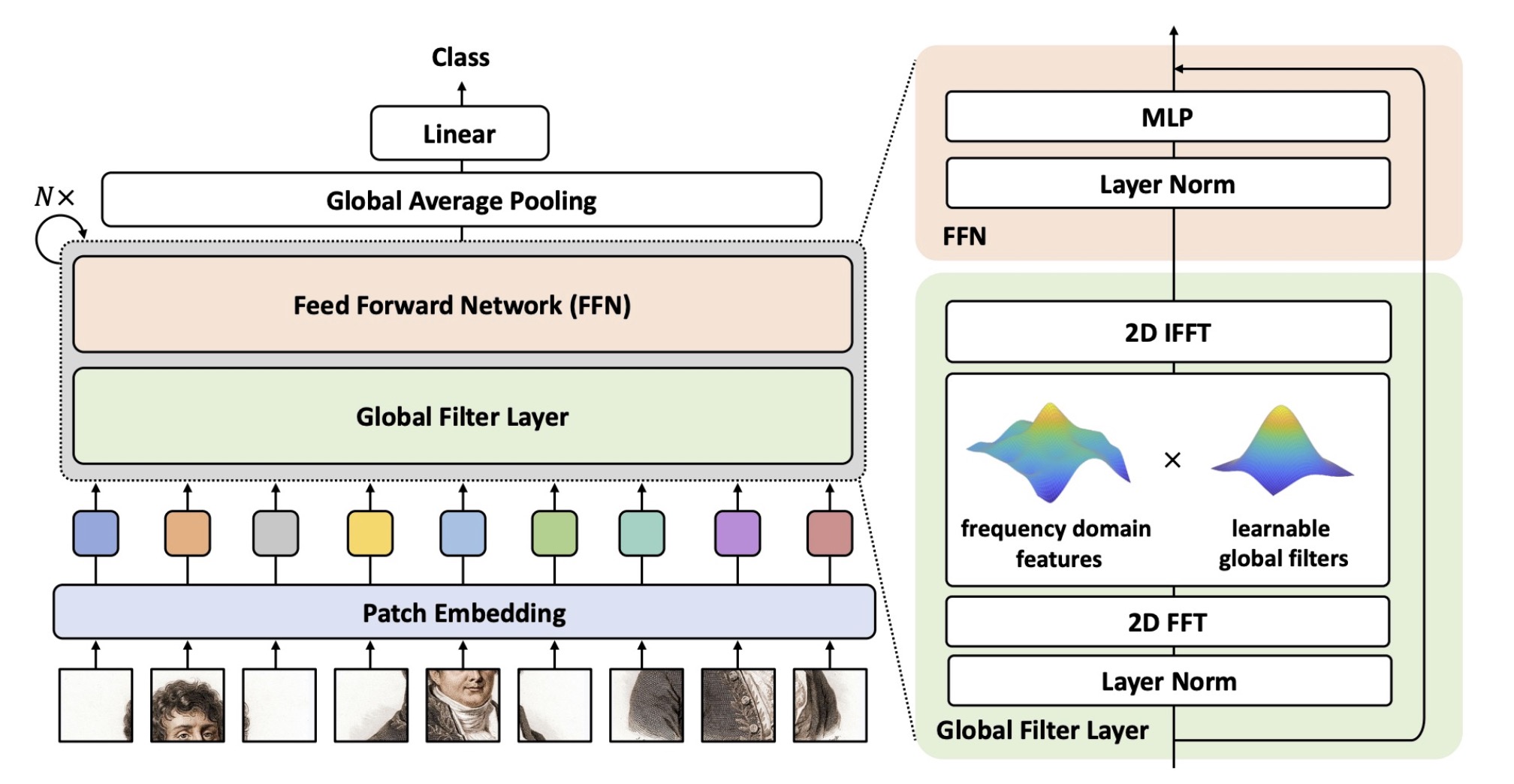
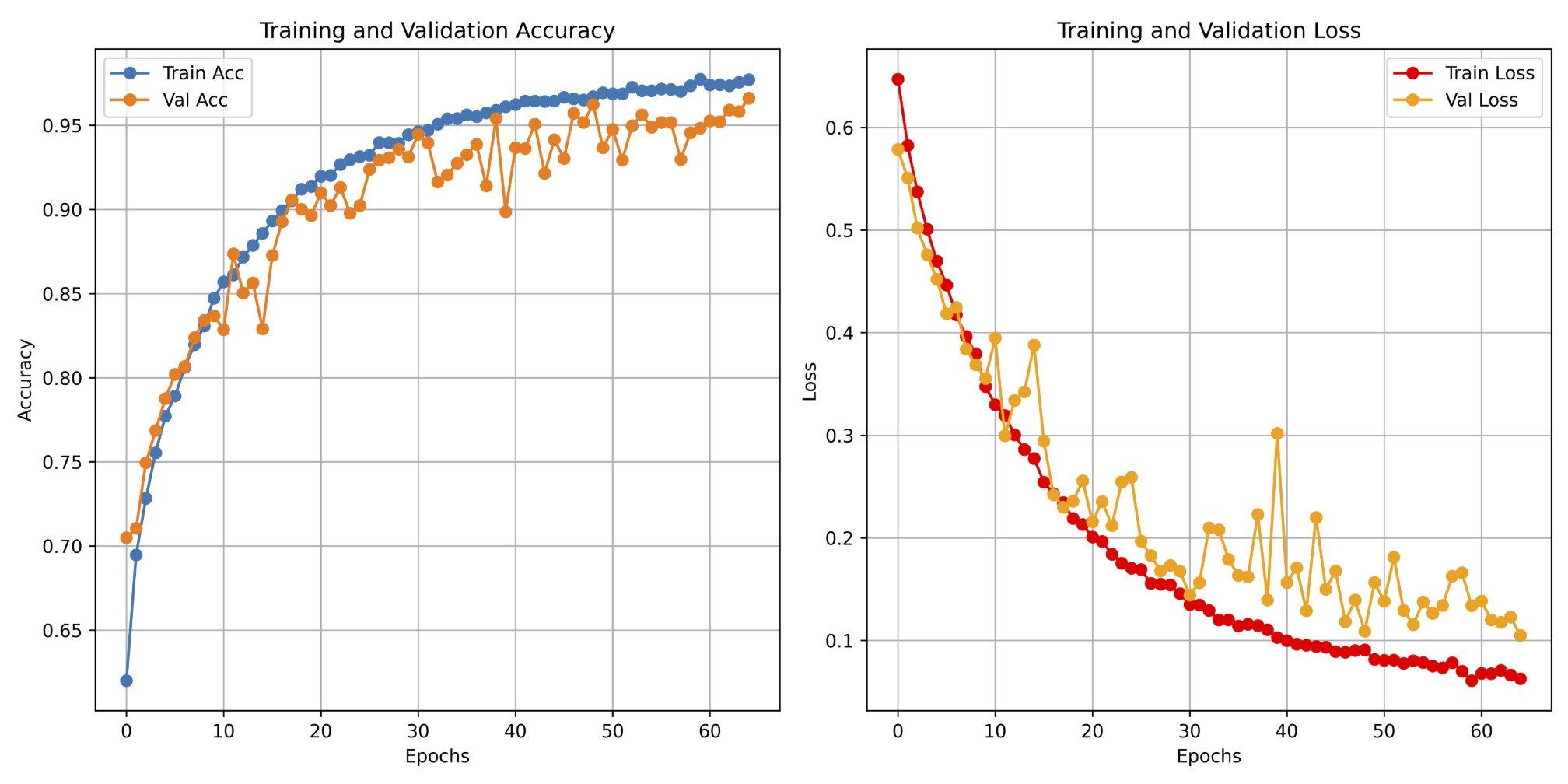
The project focuses on utilizing the advanced deep learning architecture GFNet to determine whether brain slices from the ANDI dataset indicate Alzheimer's disease. GFNet uses Fourier global filters to extract image features. The project applies GFNet to recognition tasks, handling datasets that involve pattern recognition challenges. Brain images undergo a series of data preprocessing steps. The architecture of GFNet enables the model to capture both local and global patterns in the data, providing superior performance compared to traditional neural networks. The code is modified from the original GFNet source code and was trained on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU on the University of Queensland Rangpur cluster.
- GFNet
- pytorch
- numpy
- CV2
- skLearn
- pandas
- HPC